Improving the connection range
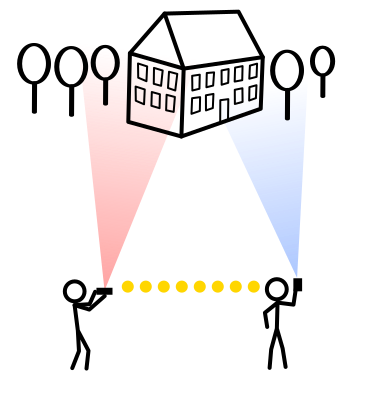
Personal hotpost to the rescue!
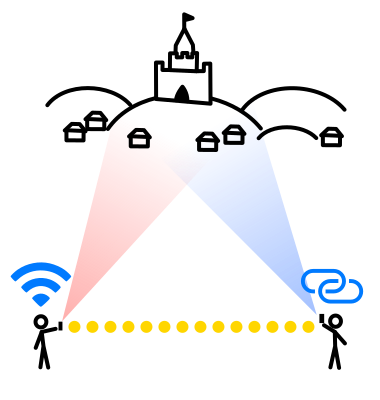
Typical distances and how to reach them
Stereoscopic vision of a typical human is only effective up to about 50 meters (160 ft). Even the modest "close range" (no Wi-Fi) connection from 3m (10 ft) away gives us the 50 times wider stereoscopic base, increasing the effective stereoscopic range up to a mile or two. This is good enough for many architectonic and natural landmarks, and sometimes even the unusually low hanging clouds. Mountain ranges and regular clouds observed closer to the horizon are much more distant: 10-30-50 miles or more. This means that the distance between the "eyes" (persons holding the phones) should be at least 50m (160 ft). This can only be achieved by connecting both devices to the same Wi-Fi network or making one device use the Personal hotspot of the other device.What is the maximum range?
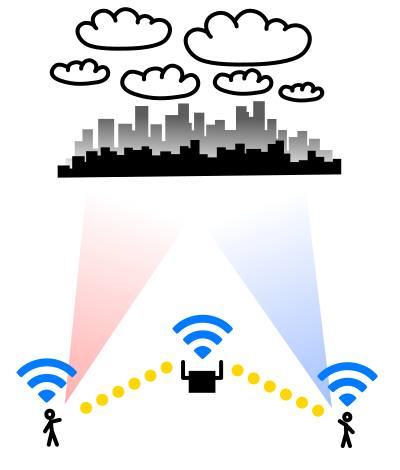
I personally managed to connect my iPad to the iPhone hotspot from about 100 meters away. I guess it was only possible thanks to being away from other Wi-Fi networks. So, don't count on such result in the city. Theoretically, the largest distances can be expected with a Wi-Fi connection through a router, or maybe even several routers serving a single network (as long as the configuration of this network allows direct connections between users). In the field, perhaps an ordinary mobile access point will give distances greater than a personal hotspot from an iPhone?
Back to introduction
